What’s Propelling Restaurant Drive-Thru Innovations?
The modern drive-thru is often traced back to Red’s Giant Hamburg on Route 66 in Springfield, Missouri, which is widely credited with pioneering a drive‑thru window in 1947. Since then, drive-thrus have become a central sales channel for quick-service restaurants (QSRs), particularly in car-centric markets like the US.
While the pandemic initially accelerated off-premises demand due to safety concerns, consumer preference for convenience has transformed this temporary spike into a lasting structural shift. By 2021, drive‑thru visits accounted for approximately 52% of U.S. off‑premises restaurant traffic, establishing the channel as a critical revenue stabilizer. Today, reliance on the drive‑thru persists not because of health anxiety, but because digital ordering and speed have become the primary drivers of guest satisfaction.
These dynamics are no longer confined to classic QSR brands; fast‑casual and full‑service chains are testing drive‑thru or pickup‑window formats to extend their off‑premises reach. Applebee’s, for example, has been adding drive‑thru pickup windows at select restaurants and has highlighted drive‑thru capabilities as a key component of its long‑term development strategy.

Source: Dine Brands Global, Inc.
For multi‑unit operators in 2025, drive‑thru performance directly influences site selection, store layout, and technology roadmaps. As the channel shifts from a marginal growth lever to a core operating capability, brands are rethinking the experience through three critical lenses, namely Speed of Service, Employee Interaction, and Order Accuracy.
Speed of Service
-
Integrated web and mobile ordering flows that route orders directly into kitchen and drive‑thru production queues.
-
AI‑enhanced digital menu and order confirmation boards that adapt in real time to demand, daypart, and promotional priorities.
-
Location‑aware apps and Bluetooth beacons that recognize guests as they arrive to surface personalized menus or loyalty rewards.
-
Multiple contactless payment options spanning mobile wallets, app‑based payment, biometrics validation, and EMV terminals at the speaker post.
-
Dynamic menus that factor in preparation complexity and real‑time inventory to prevent kitchen bottlenecks during peak periods.
-
Kitchen automation and robotics that shorten prep time and improve consistency for high‑volume items.
-
Pilots of underground conveyors and robotic delivery paths that separate food movement from vehicle traffic.
Employee Interaction
-
Gamified dashboards that make drive‑thru metrics visible to foster friendly competition among team members and locations.
-
Video management systems that capture customer interactions for coaching, quality audits, and targeted training.
-
POS workflows with guided prompts that help crew members suggest add‑ons or premium options without slowing the line.
-
Automated alerts that notify staff when guests with pre‑orders arrive at the drive‑thru or curbside pickup points.
Order Accuracy
-
Computer vision tools that monitor order assembly and packaging in real time, flagging potential mismatches before orders leave the window.
-
Improved audio systems with noise suppression technology to reduce misheard orders at the speaker post.
-
Secure identity validation at pickup using order codes or mobile app verification to ensure the right order reaches the right guest.
Heading into 2026, the drive‑thru is no longer just a secondary revenue stream; it is a primary defense against rising operating costs. QSRs that previously invested in capacity are now accelerating automation specifically to offset persistent wage pressure and commodity inflation. These economic realities are pushing the following concepts to the forefront of restaurant innovation.
1. Expanded Drive-Thru Lanes

Source: Taco Bell
Brands like Panera, McDonald’s, Burger King, and KFC are rolling out updated restaurant designs with increased drive-thru capacity and smaller dine-in areas.
Adding additional lanes is not the only option to increase drive-thru throughput. Tim Hortons has launched tandem drive-thrus that come with two sets of digital menu boards and intercom in a single lane designed to take orders from two cars at a time.
Source: Tim Hortons
Adding additional drive-thru lanes can be challenging as restaurants have to proactively address points of customer friction, manage traffic volumes, and enable seamless integration with POS systems.
Here is an extract from an article that summarizes the real-world challenges that Schlotzsky’s experienced when they piloted a double-drive-thru, with one drive-thru on each side of the restaurant.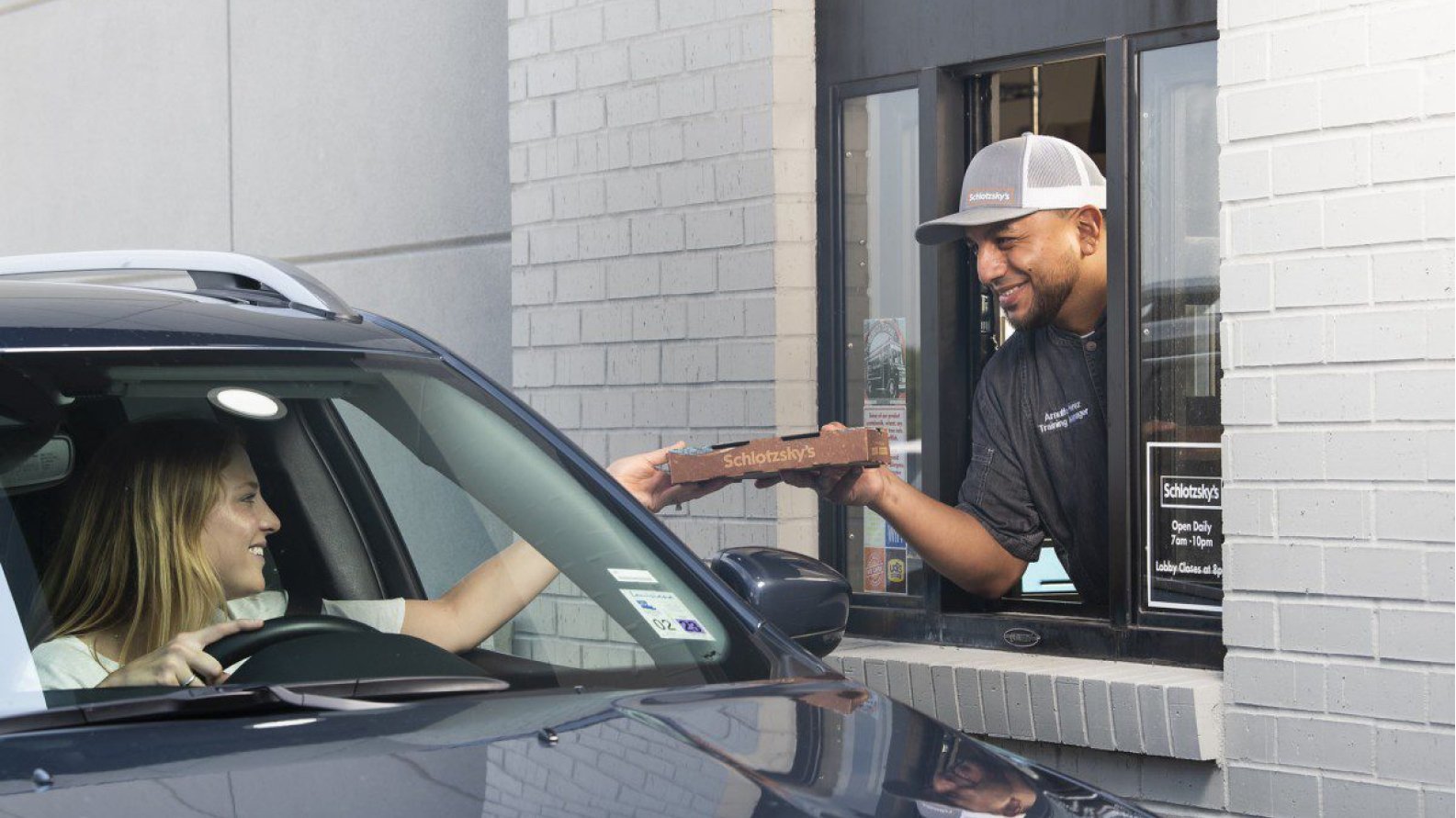
Source: Schlotzskys.com
“When you have two menu boards where you’re taking orders at the same time, we really had to figure out how that flows through into our kitchen. And when two menu boards are taking orders at the same time, we had to equip our drive-thru make station with a headset so that they could listen to both the first drive-thru lane and the second drive-thru lane, and start the production of those products before the guests finished ordering.”
“In the early days of launching this double drive-thru, Schlotzsky’s employees had to train customers that were going to the pickup lane because the service counter is now on the passenger side, which is not what customers are used to. The store needed to go back and modify signage and striping on the asphalt to make directional flow clear to customers and improve traffic confusion.”
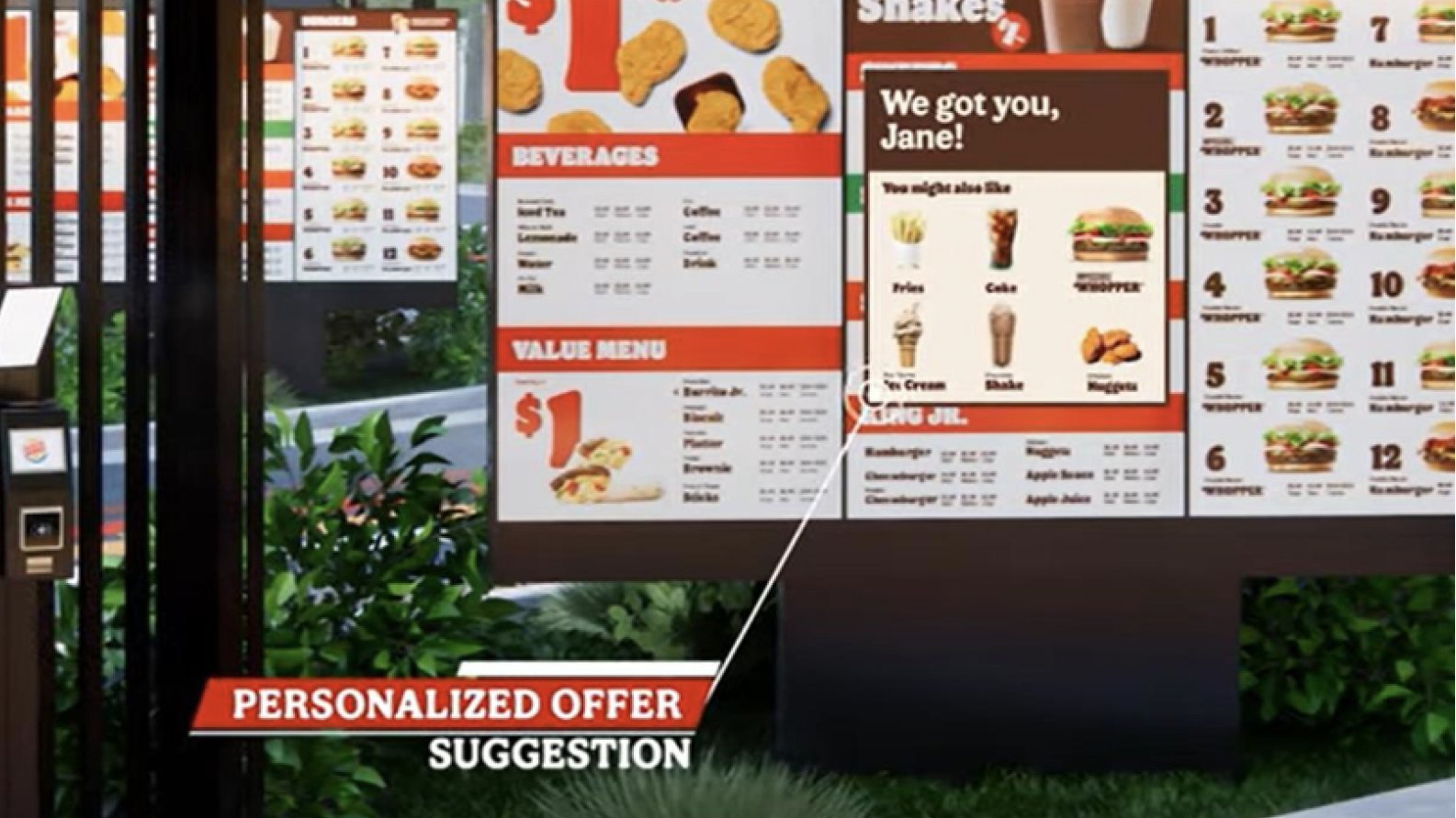
2. Intelligent Outdoor Digital Menu Boards (ODMBs)
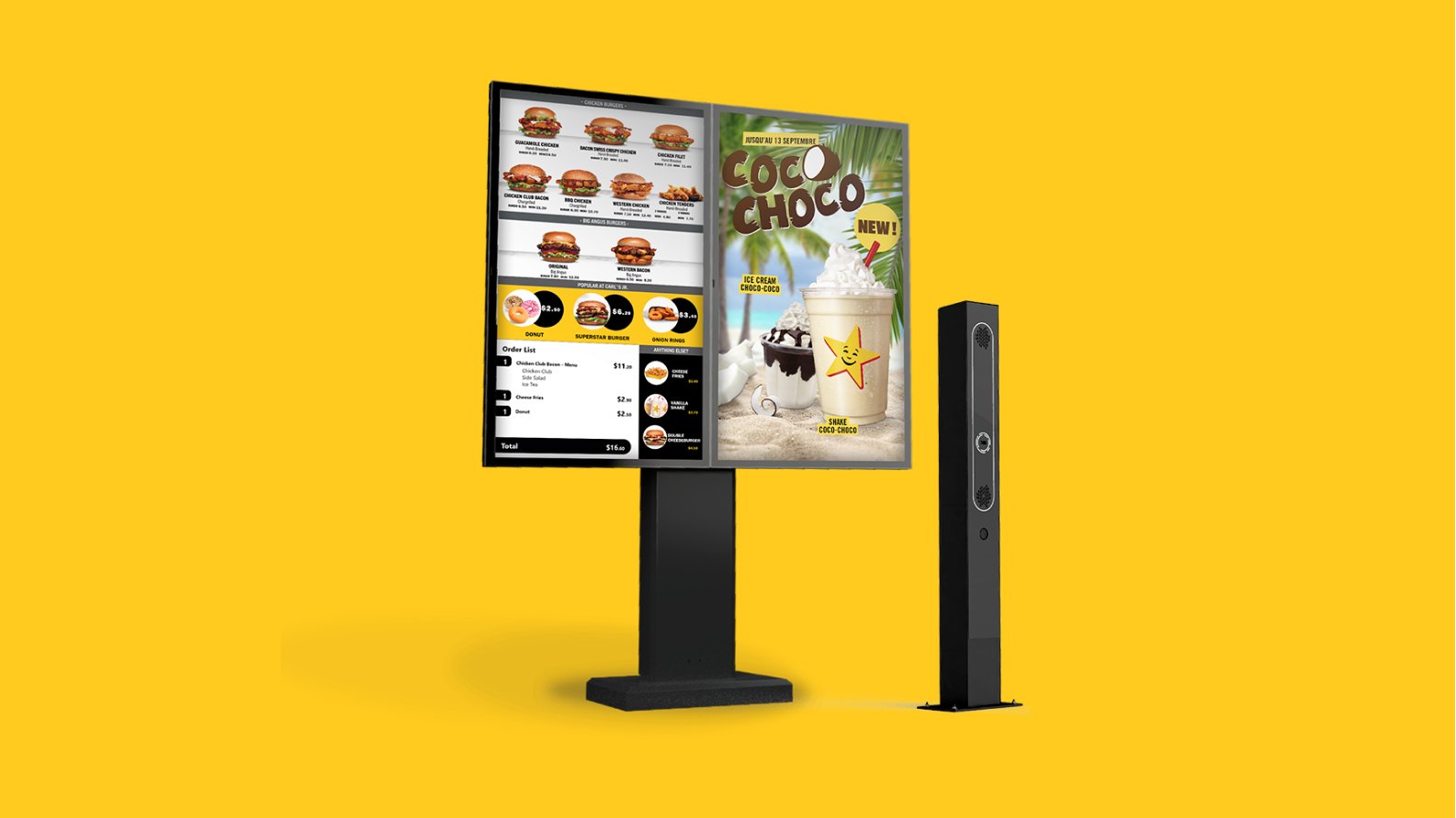

Source: Acrelec.com
Some of the recent innovations in personalizing the drive-thru experience include
- Digital menu boards linked to mobile apps that rely on the phone’s location data to trigger menu board personalization when the customer drives up to the restaurant location.
- Speciality Bluetooth devices integrated with the drive-thru speaker post to trigger menu board personalization, enable the customer to redeem reward points, and make payments using their mobile phone.
- Machine learning-driven menu boards not only suggest a personalized menu based on the purchase history, external factors (such as the weather), or daypart, but also optimize the menu to eliminate order processing complexity.
McDonald’s implemented Dynamic Yield’s personalization platform to offer a dynamic menu at their drive-thrus. In the US, McDonald’s is able to show menu items based on factors such as time of day, real-time restaurant traffic information, and popularity to help provide an enhanced customer experience. Dynamic Yields claims the pilot program was successful as McDonald’s rolled out the solution to 12000 drive-thru locations in a 6-month time period.
Restaurant Brands International, the parent company of QSR brands such as Burger King, Tim Hortons, and Popeyes had already started rolling out personalized ODMBs in 2021 across thousands of locations.
Source: Restaurants Brands International
3. Gamification for Drive-Thru Employees
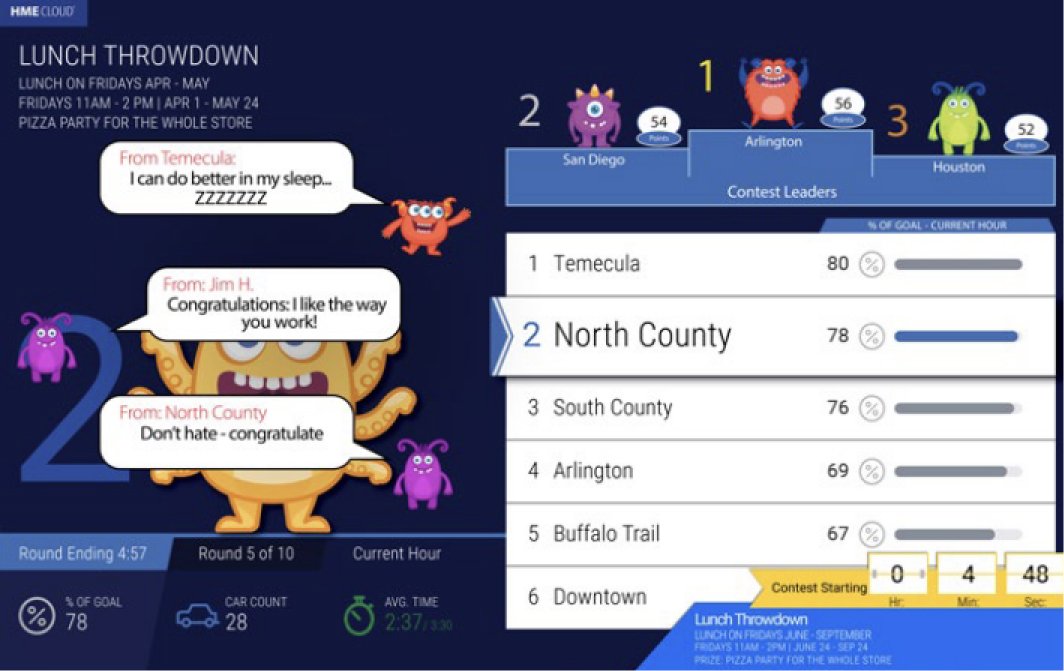
HME’s ZOOM Nitro’s drive-thru optimization system allows restaurants to gamify drive-thru service for engaging employees.
Source- Drive-thru leader boards can show where employees stand compared to their colleagues and introduce a positive competitive spirit at work.
- Restaurant chains can conduct friendly contests between locations with bragging rights and offer rewards as an upside for top-performing locations.
- As critical metrics are now transparent and available for all employees in real-time, employees readily take ownership of performance improvement plans.
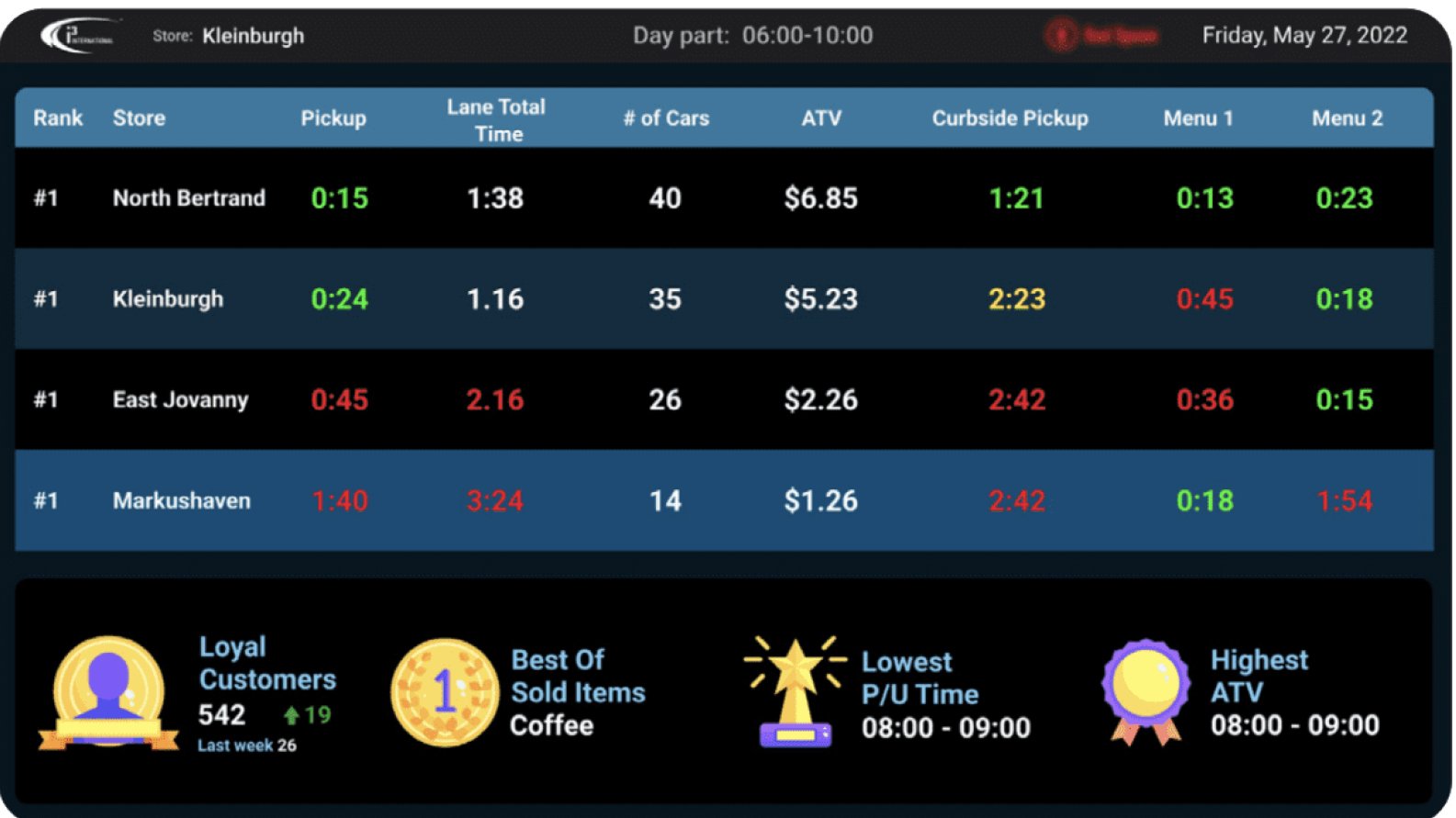
Source: Wobot
4. Computer Vision and Video Analytics at the Drive-Thru
- Computer vision can read license plates of cars and even identify the age profile of the occupants inside the car. This data is useful to recognize repeat customers and show a personalized menu or offer exclusive perks as the customer pulls into the drive-thru digital menu post.
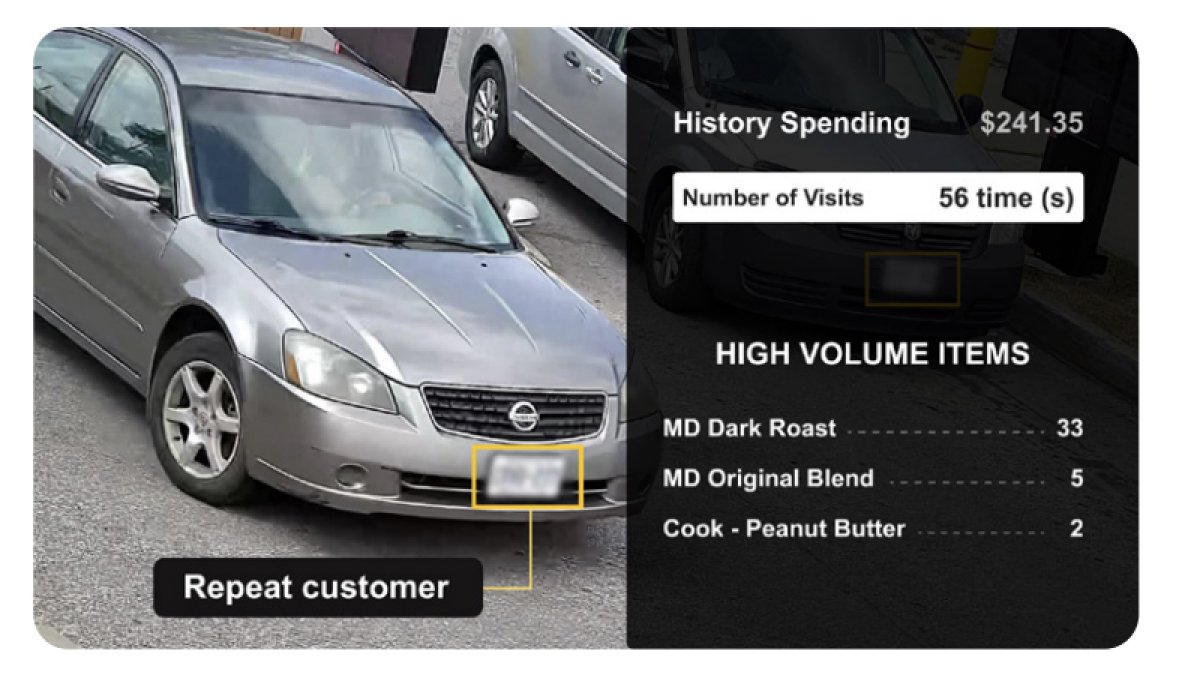
Source: Wobot
2. Ensuring order accuracy has a direct impact on sales performance and customer loyalty. Computer vision and AI applications connected to cameras in the kitchen can pinpoint mismatches in order assembly before the items are delivered to the customer.
3. In addition to identifying customers, computer vision can track drive-thru line dropout data. This information when mapped to dayparts, locations, weather, and day of the week can uncover valuable insights for QSRs. These insights can help restaurants optimize menu complexity and staffing, or even re-design the drive-thru lanes.

Presto Vision’s software allows restaurants to improve drive-thru sales and delight customers.
Source5. AI-Based Voice Assistance
- Reduce outbound (kitchen noise) and inbound noise (traffic or engine sounds), to improve order accuracy and eliminate delays due to miscommunication or poorly understood order details.
- Use automated audio alerts for employees to manage customers at the drive-thru, curbside pickup slots, or 3rd-party delivery pickups.
With AI-enabled voice technology, voice can now go beyond just improving communication. It can potentially reduce the need for employees to handle all the drive-thru transactions. This is especially useful in a tough labor market where staffing and retention are significant challenges confronting QSRs. According to SoundHound, a company that offers AI-based voice ordering solution, their technology can speed-up drive-thru order fulfillment by 10%.
Here are the various ways AI-enabled voice automation is being used by QSRs and fast-casual restaurants.
- Chipotle had already rolled-out Amazon Alexa reordering skill way back in 2019 for Chipotle customers who are already a part of the loyalty program. They later expanded AI-based voice ordering for phone orders as well. With the recent roll-out of dedicated drive-thru pick-up windows (aka Chipotlanes), Chipotle customers who order ahead using voice or app can drive up to the pickup window and drive out in under 12 seconds.
- In 2019, McDonald’s acquired Apprente, an AI-based technology that can engage in conversations with humans to improve drive-thru order accuracy. McDonald’s piloted the technology in 2021 at 24 drive-thrus in the Chicago area and reported about an 80% success rate. The technology is being further tested and upgraded with the help of IBM before a system-wide roll-out.
- Wendy’s is leveraging Google Cloud to roll out a combination of AI-enabled voice technology along with computer vision that’s designed to take orders at the drive-thrus and send the transcribed order details directly to the kitchen and POS.
Presto claims to offer AI-enabled conversational technology that can only take drive-thru orders but also upsell, recommend items with shorter preparation time, and recommend items based on past orders. The Presto voice solution has diverse applications that go beyond drive-thru. These include inventory management, phone orders, tableside ordering, and staff training.
6. Automated Drive-Thru For App Orders
“McDonald’s is piloting a drive-thru concept that completely eliminates the need to have any customer-facing staff. Customers who choose to dine in, place orders via self-service kiosks, and robots bring the order from the kitchen. For those who want to use the drive-thru, the only option available is by ordering ahead via the app.
When customers order ahead via the McDonald’s app with push notifications enabled and location access turned on, food preparation is timed to the customer’s estimated pick-up time. Once the customer reaches the restaurant, they pull into the order ahead drive-thru lane to pick up their order that’s delivered via conveyor belt.

McDonald’s is piloting an automated order ahead drive-thru lane at one of their Texas locations.
Source: McDonald’s
7. Restaurant Robotics & Future Contactless Drive-Thru
The National Restaurant Association (NRA) paints a grim view of the labor shortages that continue to plague the restaurant industry in the US. According to NRA, labor shortages remain a critical challenge for U.S. restaurants in 2024. Seven in ten operators report hiring difficulties, with nearly half saying they lack adequate staff to meet customer demand. Most understaffed locations are operating with teams at least 10% below needed levels, forcing many to reduce their hours.
To combat this challenge, some restaurants have already started deploying robots not only for kitchen automation but also for customer service. It’s just a matter of time before drive-thru customers have an entirely contactless experience when kitchen automation and service automation technologies mature.
A new crop of restaurant robot companies have all graduated their products from the design or prototyping phase to deployment at restaurants.
- Robotic Arms – Ally, Nala, Miso
- Bartender Robots – Makr Shakr, Cecilia.ai
- Bowls and Salad Maker Robots – Chowbotics, Spice, Beastro, Autec
- Food Delivery Robots – Starship, Neuro, Kiwibot
- Robot Waiters – Bellabot, Matradee, Servirobot
- Pizza Robots – Picnic, Piestro, Zume
- Coffee Shops – Cafex, Rozum, Artly, CookRight
Prominent restaurant brands are piloting robots or have already deployed them in the first set of locations.
Sweetgreen launched its Infinite Kitchen technology at its Naperville, Illinois restaurant which leverages automation to dispense greens and other ingredients precisely in bowls moving along in an assembly line.
Other established restaurant brands such as Chipotle, White Castle, and Wing Zone have all deployed Flippy, a kitchen robot that automates fast food preparation. In fact, White Castle made an announcement that it’s rolling out Flippy in one third of its nearly 350 locations.
New restaurant brands, such as Kerner, that put kitchen automation first with minimal employee presence seem to have ironed out the initial glitches and are now planning to expand in 2025.
8. Biometric Payment Lanes
QSR brands like Steak ‘n Shake and Whataburger are piloting biometric systems for faster drive-thru checkout, using facial recognition and palm vein scanning. Steak ‘n Shake is expanding pilots to 300+ locations, while Whataburger tests face/palm ID integration.
J.P. Morgan’s Paypad terminals provide the hardware backbone, supporting infrared palm vein authentication for QSR foodservice pilots ahead of 2026 rollout. These pilots address throughput bottlenecks but require privacy safeguards and AI liveness detection.
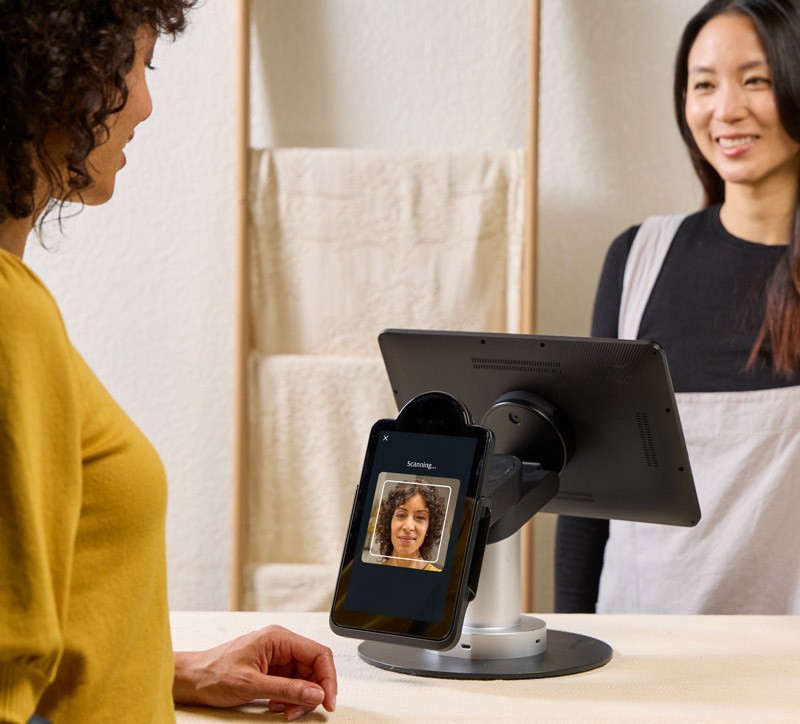

Industry forecasts show that biometrics are on track to become a mainstream way to pay rather than a niche experiment. The wider biometric payments market is expected to grow to roughly 67 billion USD by 2029, fuelled by contactless and mobile‑first experiences.
For QSRs, this trajectory strengthens the case for running tightly scoped biometric pilots in 2026 so they are ready to plug into these emerging “pay‑by‑me” models as they mature.
9. Underground Order Delivery Systems
The drive-thru experience is getting a major underground makeover as quick-service restaurants (QSRs) look to speed up their service. Restaurants are exploring underground delivery systems that create a smoother journey from kitchen to car. These underground solutions are designed to tackle several key challenges:
- Keep cars moving while orders flow smoothly from kitchen to pickup point.
- Offer a touch-free experience that many customers now prefer, especially during rush hours or when restaurants are short-staffed.
This isn’t just sci-fi fantasy – QSRs are already testing ways to move food underground using everything from conveyor belts to pneumatic tubes and specialized tunnels:
- Wendy’s made waves in 2023 by partnering with robotics startup Pipedream to test an underground “instant pickup” system at select Ohio locations. Their setup uses compact tunnels to zip sealed food containers from kitchen to driveway portal.
- Shake Shack’s 2024 partnership with Serve Robotics brought autonomous sidewalk delivery robotsto Los Angeles. These little helpers cruise the sidewalks, delivering orders within a few-mile radius. Taking it even further, Serve Robotics is working with Wing(Alphabet’s drone delivery venture) to explore combining robots and drones for delivery.
From cutting down on repetitive tasks to keeping those drive-thru lanes moving during the lunch rush, these innovations could completely transform how we grab our favorite fast food. The traditional drive-thru window might soon join the paper menu in the history books of fast-food evolution.
Groundwork Needed for Drive-Thru Innovation
There are some critical issues in the QSR industry that can potentially derail new drive-thru initiatives. Interface recommends restaurant brands to carefully consider some of these challenges proactively before expanding drive-thru operations.
1. Network Capacity
Designing the physical space and logistics of managing the traffic often takes center stage in drive-thru design while the network side of the solution may take a backseat. Network design and capacity to support mobile POS transactions, sophisticated IP cameras with edge computing capabilities, intelligent ODMBs, order confirmation systems, and perimeter security sensors (such as alarm systems) play a critical role in the successful implementation of cutting-edge drive-thru concepts.
2. Network Security
3. Accidents and Claims
4. Backend Bottlenecks
5. Security Vulnerabilities
When expensive gear, such as EV charging infrastructure, sensors, and digital boards, makes its way into the drive-thru area, it creates significant challenges for loss prevention teams. There is also a need to guard the facility against vandalism, homeless encampments, and break-ins/damage to equipment. QSRs may have to evaluate solutions such as the Virtual Perimeter Guard and Virtual Guard to proactively tackle these threats while keeping operating costs low.
6. Operational Complexity
The US has over 195000 QSRs and most of them are franchise locations. While the franchising model offers a proven brand and template for growth, key network and security infrastructure are managed by the franchise owners. This creates operational complexity as standards of implementation and solutions may vary across the chain which imposes barriers to innovation.
10. The "Energy-Thru" Evolution
Brands like Bojangles and Starbucks are redefining the “drive-thru” by turning parking spots into “Energy-Thrus” where customers can rapid-charge their Electric Vehicles (EVs) while they eat. This shifts the QSR model from pure throughput optimization to monetizing dwell time, as 20-30 minute charge times perfectly align with the dining duration.
The EV charging infrastructure being rolled out integrates with the restaurant ordering system and also offers WiFi for customers. Offering EV owners charging infrastructure is not a new concept. Subway and Taco Bell experimented with this concept several years ago. Renewed interest in the “Energy-Thru” concept is dictated by much wider adoption of EVs and a greater emphasis on sustainability.
Starbucks has partnered with Mercedes-Benz High-Power Charging to launch a charging network along the I-5 corridor, designed to provide a premium, reliable charging experience that integrates seamlessly with the coffee run.
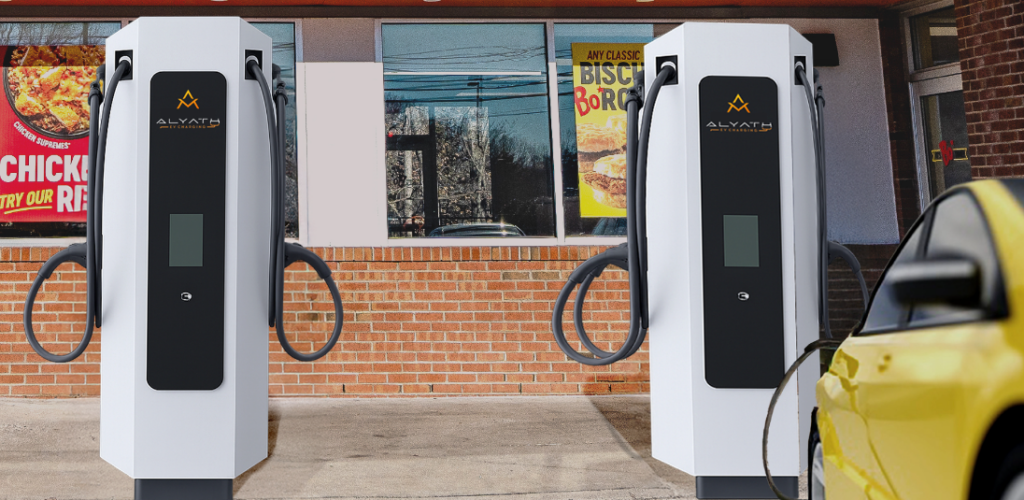

Deploying EV charging infrastructure introduces new operational complexities. Restaurants must now manage outdoor network stability for payment processing and ensure physical security for expensive charging hardware.



